The Evolution of Resealable Packaging
Resealable packaging has evolved from a convenience feature into a strategic packaging solution that enhances product freshness, reduces food waste, and improves the consumer experience. Today, it plays a critical role across food, personal care, pharmaceuticals, and e-commerce. This blog explores how resealable packaging has evolved over time, the materials and technologies behind it, and where it is most effectively used today.
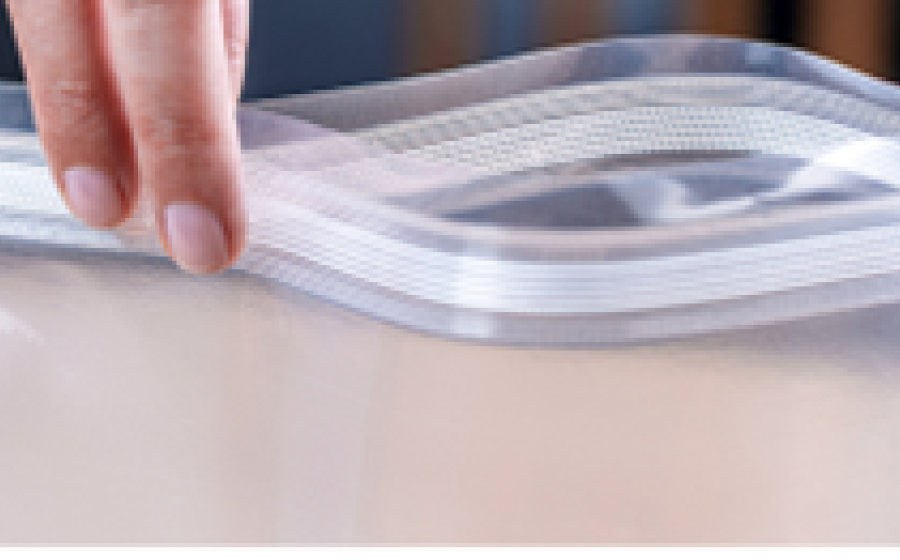
Any package designed to be opened and securely closed multiple times without compromising product integrity can be considered a resealable package. Unlike single-use seals, resealable systems allow consumers to access products in portions while maintaining freshness and protection throughout the product lifecycle.
Early Beginnings of Resealable Packaging
The earliest forms of resealable packaging were simple mechanical solutions. Metal tins with friction lids, glass jars with screw caps, and paperboard cartons with tuck-in flaps dominated early markets. While functional, these formats offered limited barrier protection and were not ideal for lightweight or flexible packaging applications.
The real shift began in the late 20th century with the rise of plastic films and flexible packaging. As consumer lifestyles changed and demand grew for convenience foods and portable products, packaging needed to adapt.
Materials Used in Resealable Packaging
Material innovation has been central to the evolution of resealable packaging. Today’s solutions balance barrier performance, machinability, consumer usability, and sustainability.
Plastic Films and Laminates
Plastic remains the most widely used material for resealable packaging due to its flexibility and seal integrity. Common materials include:
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) for zipper profiles
- Polypropylene (PP) for improved stiffness and heat resistance
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) for strength and clarity
- Multilayer laminates combining PE, PET, EVOH, or nylon for enhanced oxygen and moisture barriers
These structures are commonly used in food, pet food, and household products.
Paper and Fiber-Based Materials
In response to sustainability demands, paper-based resealable packaging has gained traction. These solutions often use:
- Coated or laminated paper with bio-based or water-based barrier layers
- Fiber-based structures with integrated zipper systems
- Hybrid paper plastic designs that reduce overall plastic content
While fully plastic-free resealable systems remain challenging, notable progress is being made in dry food and snack applications.
Bio-Based and Compostable Materials
Compostable resealable packaging is emerging, particularly for organic and premium brands. Materials such as PLA, cellulose films, and bio-PE are being explored, although achieving consistent reseal performance and shelf life remains a technical challenge.
Key Technologies Behind Resealable Packaging
Technological innovation has transformed resealable packaging from basic closures into highly engineered systems.
Press-to-Close Zippers

One of the most common resealable technologies, press-to-close zippers are widely used in flexible pouches. These systems offer:
- Ease of use
- Reliable reseal performance
- Compatibility with high-speed packaging lines
They are especially popular in snack foods, frozen foods, and pet food packaging.
Slider Zippers

Slider mechanisms improve accessibility and consumer convenience. They are commonly used for larger packs or products requiring frequent access. While more expensive, they offer strong differentiation and premium appeal.
Hook-to-Hook and Interlocking Profiles

Advanced zipper profiles provide stronger seals and improved contamination resistance. These are increasingly used in medical, pharmaceutical, and industrial packaging where product protection is critical.
Peel and Reseal Adhesives

Peelable reseal systems use pressure-sensitive or heat-activated adhesives that allow consumers to reseal a package multiple times. These are common in:
- Fresh produce
- Bakery items
- Ready-to-eat foods
This technology enables flat packaging formats without the need for zipper insertion.
Laser Scoring and Easy-Open Features

Laser scoring ensures clean initial opening without damaging the reseal mechanism. This improves consumer experience and reduces frustration associated with tearing flexible packs incorrectly.
Use Cases Across Industries
Food and Beverage Packaging
Food remains the largest application for resealable packaging. Use cases include:
- Snacks, nuts, and confectionery
- Cheese, deli meats, and frozen foods
- Coffee and powdered beverages
Resealable packaging helps maintain freshness, control portion sizes, and reduce food waste.
Pet Food and Animal Nutrition
Large pack sizes and frequent use make resealability essential in pet food. Zippered pouches and slider systems are now standard across premium and mass-market brands.
Personal Care and Home Care
Wet wipes, detergents, and personal hygiene products rely on resealable packaging to prevent moisture loss and contamination. Durable reseal performance is critical in these applications.
Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare
In healthcare, resealable packaging supports compliance, safety, and hygiene. Examples include:
- Unit-dose medical devices
- Diagnostic kits
- Nutraceuticals and supplements
E-Commerce and Subscription Packaging
With rising direct-to-consumer models, resealable packaging is being used to enable returns, refills, and reuse, aligning with circular economy principles.
Sustainability and the Future of Resealable Packaging
The future of resealable packaging lies in making these systems more recyclable and material efficient. Current innovation focuses on:
- Mono-material zipper systems compatible with recycling streams
- Reduced material weight without compromising seal integrity
- Design for recyclability and circular packaging models
Brands and packaging converters are also exploring reusable and refillable formats where resealability becomes a core functional requirement rather than a secondary feature.
Resealable packaging has come a long way from basic closures to advanced, consumer-centric systems. Driven by material science, engineering innovation, and evolving consumer behavior, it continues to redefine how products are protected, consumed, and reused. As sustainability and convenience remain top priorities, resealable packaging will play an increasingly critical role in the future of packaging design.