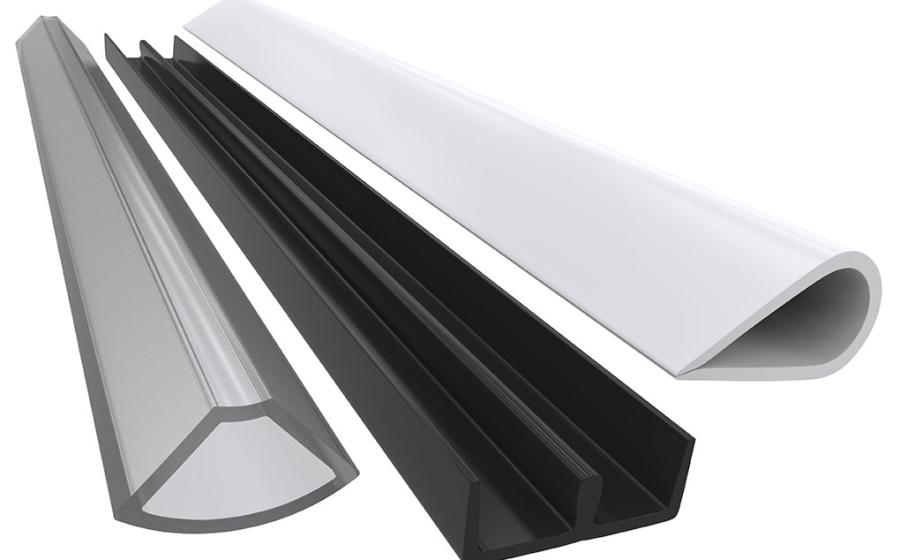
Packaging plays a major role in protecting products, enhancing their shelf life, and presenting them to customers in the best way possible. Among the many options available, plastic profile extrusion stands out as a popular choice for many industries. It's flexible, cost-effective, and highly customizable. However, selecting the right type of extrusion can be challenging without understanding the basics. This guide will walk through the essential factors to consider when choosing the right plastic profile extrusion for packaging.
What Is Plastic Profile Extrusion?
Plastic profile extrusion is a manufacturing technique used to form plastic into continuous shapes with a consistent cross-section. The process begins by heating plastic resin until it melts, then pushing it through a specially designed mold, or die, to achieve the desired shape. Once formed, the profile is cooled and trimmed to specific lengths. This method is commonly used to create products such as protective edges, tubing, signage strips, and custom structural elements for packaging.
Because it's a continuous process, it works well for high-volume production. It also offers precision, making it easier to meet unique packaging needs. To get the best results, it's often wise to work with plastic profile extrusion companies that specialize in custom solutions. These partners can guide the material selection, assist with profile design, and ensure the final product meets both functional and visual requirements.
Why Plastic Extrusions Work Well in Packaging
Plastic profile extrusions are favored in packaging for several reasons:
- Durability: Plastic is strong enough to handle impacts, bending, and rough handling.
- Lightweight: It adds minimal weight to the product, which helps reduce shipping costs.
- Moisture resistance: Plastic doesn't absorb moisture, making it ideal for protecting products from humidity.
- Design flexibility: Different shapes, sizes, and colors can be created without extra tools or processes.
For example, clear plastic channels are often used to hold labels or price tags in retail displays. Foam-backed profiles can cushion fragile items during transport. The versatility of plastic extrusion opens up endless design possibilities.
Consider the Type of Plastic Material
Choosing the right material is one of the most important decisions. Different types of plastic offer different strengths, levels of flexibility, and resistance to chemicals or temperature.
Here are some common choices:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Tough, affordable, and resistant to moisture. Good for structural packaging elements like edge trims.
- Polyethylene (PE): Lightweight and flexible. Works well in temporary or disposable packaging.
- Polypropylene (PP): Offers good chemical resistance and durability. Often used in food-safe applications.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its toughness and impact resistance. Suitable for reusable or heavy-duty packaging.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): Flexible like rubber. Ideal for seals or gaskets in packaging that need to be airtight.
Understanding what the packaging will go through—such as exposure to heat, pressure, or chemicals—can help narrow down the right material.
Think About the Shape and Function
The shape of the extrusion should support the purpose of the packaging. A U-shaped profile might be perfect for holding a product in place, while a flat strip may work better for securing edges.
Here are a few functional questions to ask:
- Does the profile need to lock two parts together?
- Will it act as a cushion, spacer, or guide?
- Is transparency important for visibility or branding?
A good design not only protects the product but also makes it easier to store, display, or transport.
Customization Options
Many manufacturers offer custom tooling for unique packaging needs. Colors can match branding, and profiles can include logos or textured finishes. Some even provide co-extrusion, where two or more materials are combined into one profile for added performance—such as combining a rigid plastic with a soft rubber seal.
Custom extrusion may involve extra time and setup costs, but the end result can be worth it, especially for large production runs or special product lines.
Consider the Environment and Recyclability
As businesses focus more on sustainability, it's important to choose materials that align with eco-friendly goals. Some plastics, like polyethylene and polypropylene, are easier to recycle than others.
Also, consider reducing material use where possible. Thinner walls, fewer layers, or choosing recyclable over single-use materials can help reduce environmental impact without sacrificing performance.
Volume and Budget Constraints
Production volume directly affects cost. Standard profiles in popular materials are usually more budget-friendly. On the other hand, custom profiles may come with higher upfront costs but lower unit costs over time.
Ask suppliers about minimum order quantities and whether they already have tooling for your desired profile. This can help save time and money, especially during the development stage.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Before committing to a supplier, check their quality control measures. Do they test for consistency, dimensions, or durability? Can they meet industry standards or certifications if required?
Reliable suppliers will offer samples and may even assist in product testing. Testing ensures the extrusion will perform as expected when used in real-life packaging situations.
Supplier Support and Lead Time
Lastly, consider the supplier's ability to deliver on time and offer technical support. Do they help with design adjustments? Can they scale production quickly if demand increases?

Choosing a supplier with a strong track record and good communication can make the entire process smoother.
Conclusion
Plastic profile extrusion provides a smart and flexible solution for modern packaging needs. With the right material, design, and supplier, businesses can create packaging that protects products while supporting branding and efficiency. Each decision—from shape to sustainability—plays a role in how well the packaging performs. Taking the time to consider these factors ensures better results and long-term value. Whether the goal is durability, visual appeal, or cost savings, the right extrusion choice can make a real difference.